Intent Classification

บทความโดย ผศ.ดร.ณัฐโชติ พรหมฤทธิ์
ภาควิชาคอมพิวเตอร์
คณะวิทยาศาสตร์
มหาวิทยาลัยศิลปากร
ใน Workshop นี้เราจะได้เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับการทำ Intent Classification กับ Dataset ที่เป็นประโยคภาษาอังกฤษ จำนวน 1,113 ประโยค ซึ่งมีการแบ่ง Intent ออกเป็น 21 Class โดยใช้ Model แบบ RNN ที่รับ Dataset ผ่าน Input Node แบบ Time Series หรือข้อมูลที่มีลักษณะเป็นลำดับ เช่น X0, X1, X2,... Xt
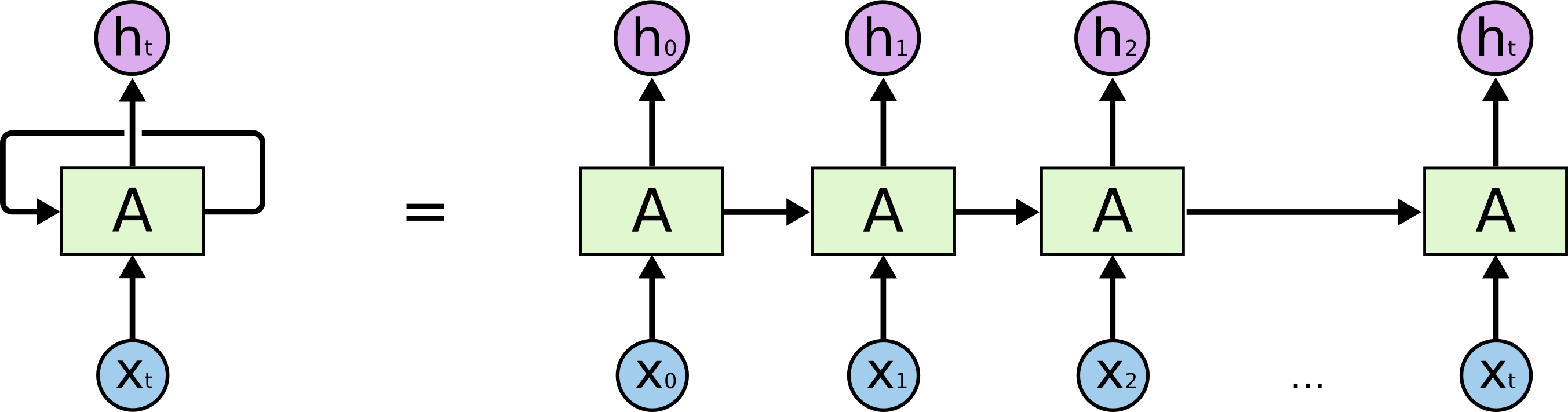
ซึ่งเมื่อมีการประมวลผลใน RNN Cell แล้ว จะมีการส่งผลลัพธ์ออกมาเป็น Vector h0, h1, h2, ..., ht ตามลำดับ โดยในการประมวลผลแต่ละรอบจะมีการนำ Output State ของ RNN Cell ในรอบก่อนหน้ามาเป็น Input State ของ RNN Cell ในรอบถัดไป
ภายใน RNN Cell จะมีวงจรสำหรับนำ Input Data x Weight ในรูปแบบต่างๆ ซึ่งปัจจุบันมีรูปแบบ RNN Cell ที่นิยม 2 รูปแบบ ได้แก่ วงจรแบบ LSTM และ GRU
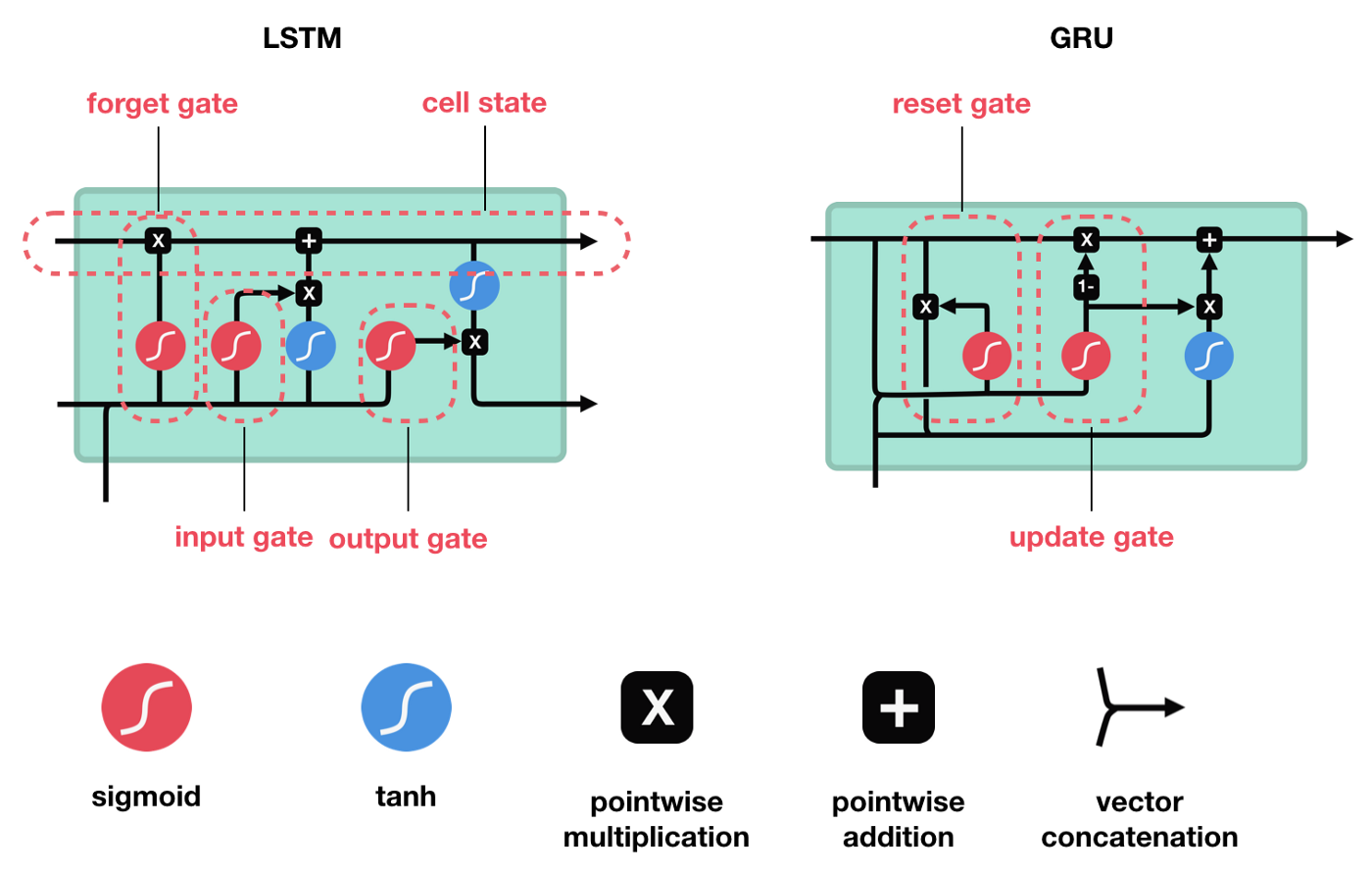
อย่างไรก็ตาม RNN Neural Network นั้นมีจุดอ่อนที่มันจะมีการสูญเสีย Information เมื่อมีการย้อนกลับไปปรับค่า Weight โดยเฉพาะถ้ามีการรับ Input Data ที่มีความยาวมากๆ ดังนั้นเพื่อลดการสูญเสีย Information ในการปรับค่า Weight เราจะประกอบ RNN Cell ในแบบ Bidirectional RNN ครับ
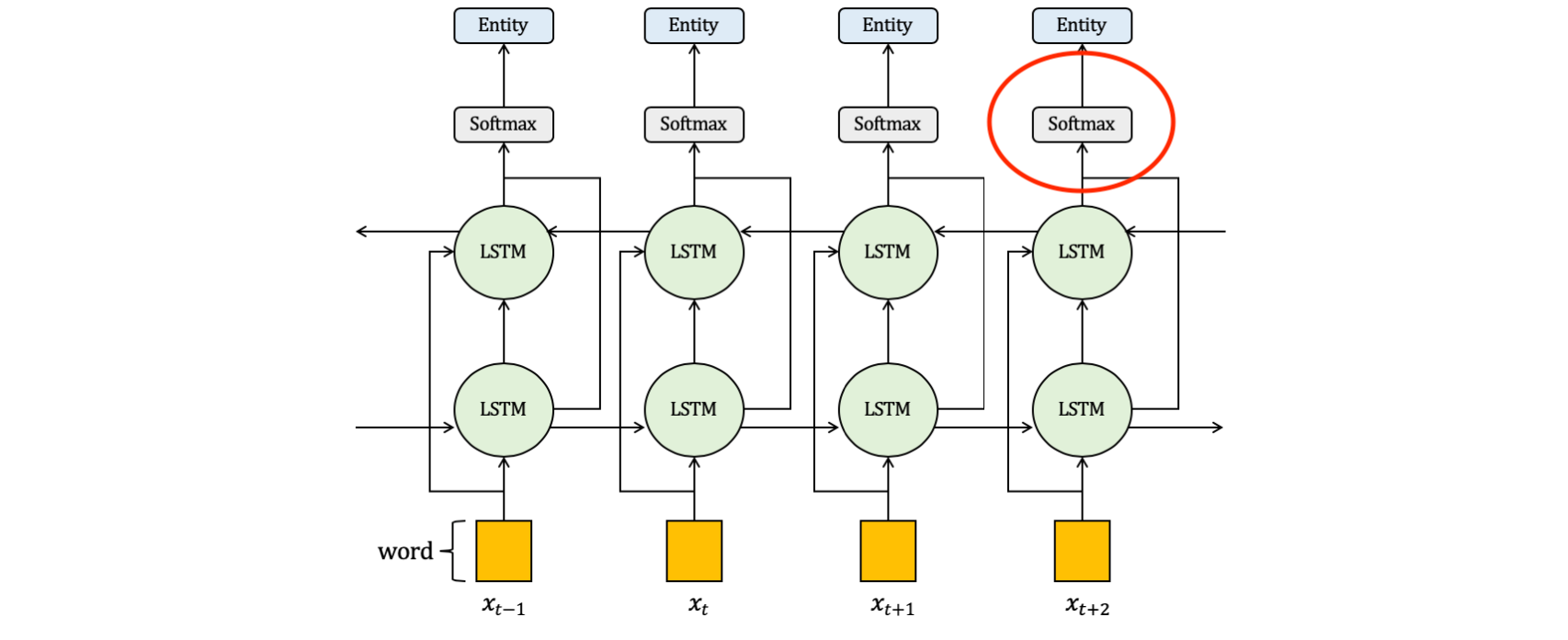
โดยใน Workshop นี้ เราจะนำค่าจาก Vector h เฉพาะ ht มาใช้ในการ Predict Intent ประโยคภาษาอังกฤษ โดยมีขั้นตอนดังต่อไปนี้
- ก่อนอื่น เราจะต้อง Import Package ที่จำเป็น
import pandas as pd
import re
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from keras_preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, GRU, LSTM, Bidirectional, Embedding, Dropout, BatchNormalization
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint
import pickle as p
import plotly
import plotly.graph_objs as go
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import seaborn as sn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report- กำหนดจำนวน EPOCHS และ Batch Size ดังต่อไปนี้
EPOCHS = 100
BS = 32- นิยาม Function สำหรับ Load Dataset ซึ่งประกอบด้วย ข้อความ (Sentence), ผลเฉลย (Intent) และรายชื่อ Intent ทั้งหมด 21 Intent (unique_intent)
def load_dataset(filename):
df = pd.read_csv(filename, names = ["Sentence", "Intent"])
print(df.head())
intent = list(df["Intent"])
unique_intent = list(set(intent))
sentences = list(df["Sentence"])
return (unique_intent, intent, sentences)- Download Load Dataset ประโยคภาษาอังกฤษ จากไฟล์ intent.csv ที่ http://gitlab.cpsudevops.com/nuttachot/intentclassification.git แล้วบันทึกไว้ใน Project kincentric_cpsu เขียน Code ตามตัวอย่างด้านล่าง กด Shift+Enter เพื่อ Load Dataset เก็บในตัวแปร unique_intent, intent และ sentences
unique_intent, intent, sentences = load_dataset("intent.csv")
- นิยาม Function เพื่อ Cleaning ประโยค โดยคัดไว้เฉพาะข้อความภาษาอังกฤษ และตัวเลข ตัดคำ แปลงเป็นตัวอักษรตัวเล็ก เก็บแต่ละคำของแต่ละประโยคไว้ใน List (temp) เพื่อหาความยาวของประโยค รวมทั้งเก็บแต่ละประโยคแบบ String (words) เพื่อสร้าง Train Data
import re
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
def cleaning(sentences):
words = []
temp = []
for s in sentences:
clean = re.sub(r'[^\w]', " ", s)
w = word_tokenize(clean)
temp.append([i.lower() for i in w])
words.append(' '.join(w).lower())
return words, temp- Clean ประโยคทั้งหมด 1113 ประโยค
import nltk
nltk.download('punkt')
cleaned_words, temp = cleaning(sentences)
print(len(cleaned_words))
print(cleaned_words[:5])
- นิยาม Function create_tokenizer เพื่อสร้าง Keras Tokenizer Object
def create_tokenizer(words, filters = ''):
token = Tokenizer(filters=filters)
token.fit_on_texts(words)
return token- สร้าง Keras Tokenizer Object ที่มีการ Train ด้วย Sentence ที่ถูก Cleaning แล้ว ซึ่งเราจะได้ Bag of Word และจำนวนคำศัพท์ของ Bag of Word จาก Keras Tokenizer ดังภาพด้านล่าง
train_word_tokenizer = create_tokenizer(cleaned_words)
vocab_size = len(train_word_tokenizer.word_index) + 1
train_word_tokenizer.word_index
- นิยาม Function เพื่อหาความยาวสูงสุดของคำในประโยค ซึ่งเราจะค้นหาประโยคที่มีความยาวสูงสูดโดยใช้ Parameter key = len และนับคำในประโยคโดยใช้ Function len
def max_length(words):
return(len(max(words, key = len)))- กำหนดความยาวสูงสุดของคำในประโยคให้กับ max_length เพื่อเตรียมทำ Padding และกำหนดจำนวน Step ของ GRU Network ซึ่งพบว่าประโยคยาวที่สุดมีความยาว 28 คำ ครับ
max_length = max_length(temp)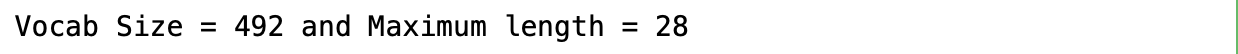
- นิยาม Function เพื่อแปลงคำภาษาอังกฤษเป็นตัวเลข
def encoding_doc(token, words):
return(token.texts_to_sequences(words))- แปลงคำในประโยคที่ได้ทำ Cleaning เป็นตัวเลข ด้วย Keras Tokenizer Object ที่ถูก Train แล้ว
encoded_doc = encoding_doc(train_word_tokenizer, cleaned_words)
print(cleaned_words[0])
print(encoded_doc[0])
- นิยาม Function เพื่อทำ Padding ตัวเลขที่แทนแต่ละคำในประโยค โดยกำหนดให้มีการเติม 0 เพื่อให้แต่ละประโยคมีความยาวเท่ากัน (28 คำ)
def padding_doc(encoded_doc, max_length):
return(pad_sequences(encoded_doc, maxlen = max_length, padding = "post"))- ทำ Padding
padded_doc = padding_doc(encoded_doc, max_length)
print("Shape of padded docs = ",padded_doc.shape)
print(cleaned_words[0])
print(encoded_doc[0])
print(padded_doc[0])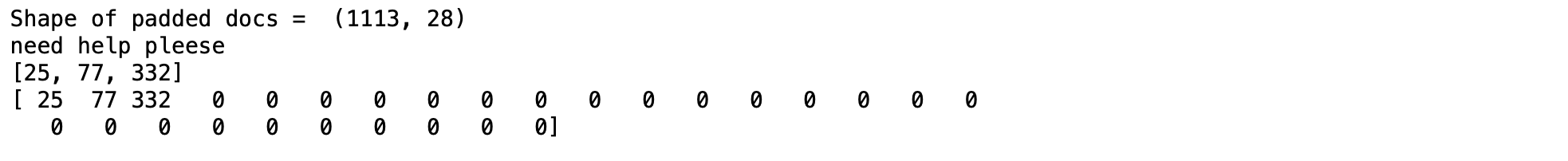
- สร้าง output_tokenizer ด้วยการ Train tokenizer ด้วยชื่อ Intent ทั้งหมด 21 Intent
output_tokenizer = create_tokenizer(unique_intent)- แปลง Intent หรือผลเฉลยเป็นตัวเลขโดยใช้ output_tokenizer
encoded_output = encoding_doc(output_tokenizer, intent)
print(intent[0:2])
print(encoded_output[0:2])
- เพิ่มมิติของผลเฉลยจาก 1113 เป็น 1113 x 1 สำหรับการเข้ารหัสผลเฉลยแบบ One Hot
encoded_output = np.array(encoded_output).reshape(len(encoded_output), 1)- นิยาม Function การเข้ารหัสผลเฉลยแบบ One Hot
def one_hot(encode):
oh = OneHotEncoder(sparse = False)
return(oh.fit_transform(encode))- เข้ารหัสผลเฉลยแบบ One Hot
output_one_hot = one_hot(encoded_output)
print(encoded_output[0])
print(output_one_hot[0])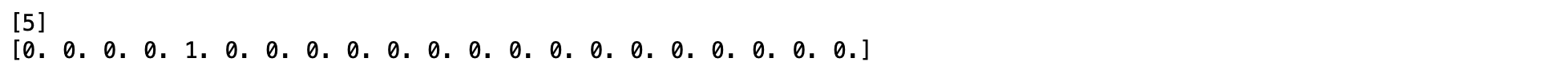
- แบ่ง Input Data พร้อมผลเฉลย (Dataset) สำหรับ Train 80% และ Validate 20% โดยใช้ Parameter แบบ Stratified Sampling เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าจะได้ Validate Dataset ที่มีข้อมูลครบทุก Intent
train_X, val_X, train_Y, val_Y = train_test_split(padded_doc, output_one_hot, shuffle = True, test_size = 0.2, stratify=output_one_hot)- Print Shape ของ Dataset
print("Shape of train_X = %s and train_Y = %s" % (train_X.shape, train_Y.shape))
print("Shape of val_X = %s and val_Y = %s" % (val_X.shape, val_Y.shape))
- กำหนดจำนวน Intent ให้กับ num_classes สำหรับนิยามจำนวน Output Node ของ GRU Neural Network
num_classes = len(unique_intent)- นิยาม Model แบบ GRU ซึ่งเป็น Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) แบบหนึ่ง
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, GRU, LSTM, Bidirectional, Embedding, Dropout, BatchNormalization
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
adam = Adam(lr=0.001, decay=0.01)
def create_model(vocab_size, max_length):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(vocab_size, 128, input_length = max_length, trainable = True))
model.add(Bidirectional(GRU(128, activation = "relu"))) # activation = "relu"
model.add(Dense(64, activation = "relu"))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(64, activation = "relu"))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(BatchNormalization())
model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation = "softmax"))
return model
model = create_model(vocab_size, max_length)- Compile และ Print ชนิดของ Layer, Output Shape และจำนวน Parameter ของ Model
model.compile(loss = "categorical_crossentropy", optimizer = 'adam', metrics = ["accuracy"])
model.summary()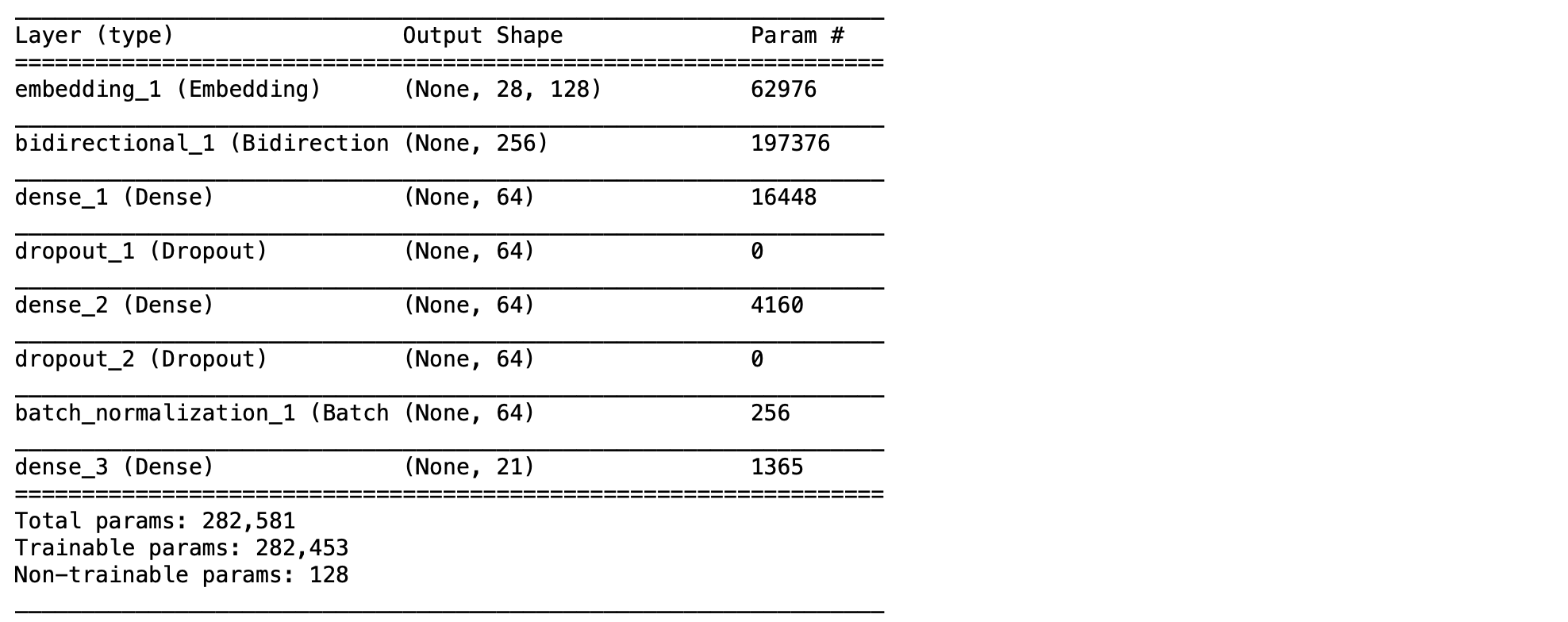
- สร้างจุด Check Point เพื่อ Save Model เฉพาะ Epoch ที่มี val_loss น้อยที่สุด
filename = 'model.h5'
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(filename, monitor='val_loss', verbose=1, save_best_only=True, mode='min')- Train Model
hist = model.fit(train_X, train_Y, epochs = EPOCHS, batch_size = BS, validation_data = (val_X, val_Y), callbacks = [checkpoint])
- Save History
with open('history_model', 'wb') as file:
p.dump(hist.history, file)- Load History
with open('history_model', 'rb') as file:
his = p.load(file)- Plot Loss และ Validate Loss
plotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)
h1 = go.Scatter(y=his['loss'],
mode="lines", line=dict(
width=2,
color='blue'),
name="loss"
)
h2 = go.Scatter(y=his['val_loss'],
mode="lines", line=dict(
width=2,
color='red'),
name="val_loss"
)
data = [h1,h2]
layout1 = go.Layout(title='Loss',
xaxis=dict(title='epochs'),
yaxis=dict(title=''))
fig1 = go.Figure(data = data, layout=layout1)
plotly.offline.iplot(fig1, filename="Intent Classification")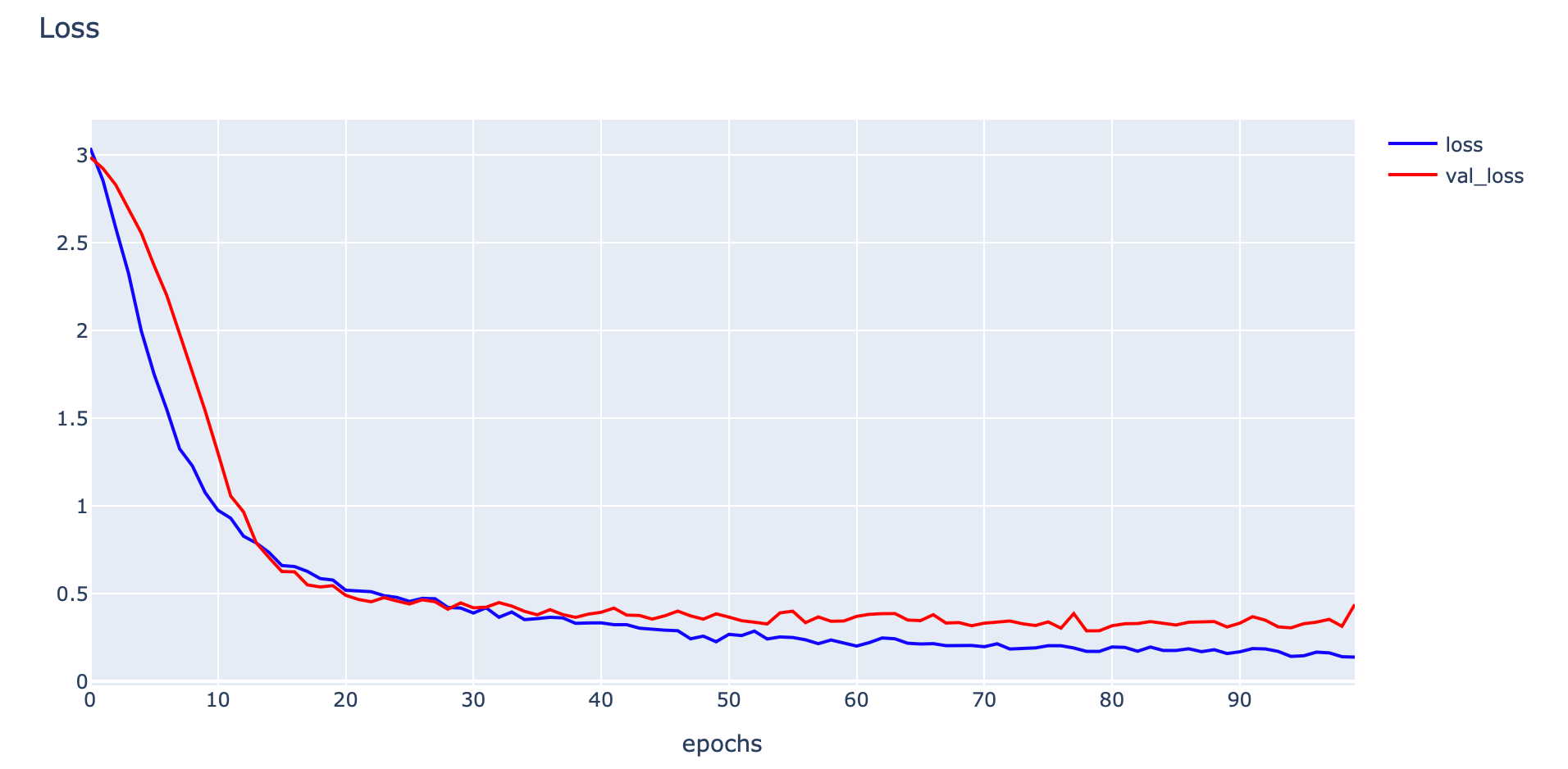
- Plot Accuracy และ Validate Accuracy
h1 = go.Scatter(y=his['accuracy'],
mode="lines", line=dict(
width=2,
color='blue'),
name="acc"
)
h2 = go.Scatter(y=his['val_accuracy'],
mode="lines", line=dict(
width=2,
color='red'),
name="val_acc"
)
data = [h1,h2]
layout1 = go.Layout(title='Accuracy',
xaxis=dict(title='epochs'),
yaxis=dict(title=''))
fig1 = go.Figure(data = data, layout=layout1)
plotly.offline.iplot(fig1, filename="Intent Classification")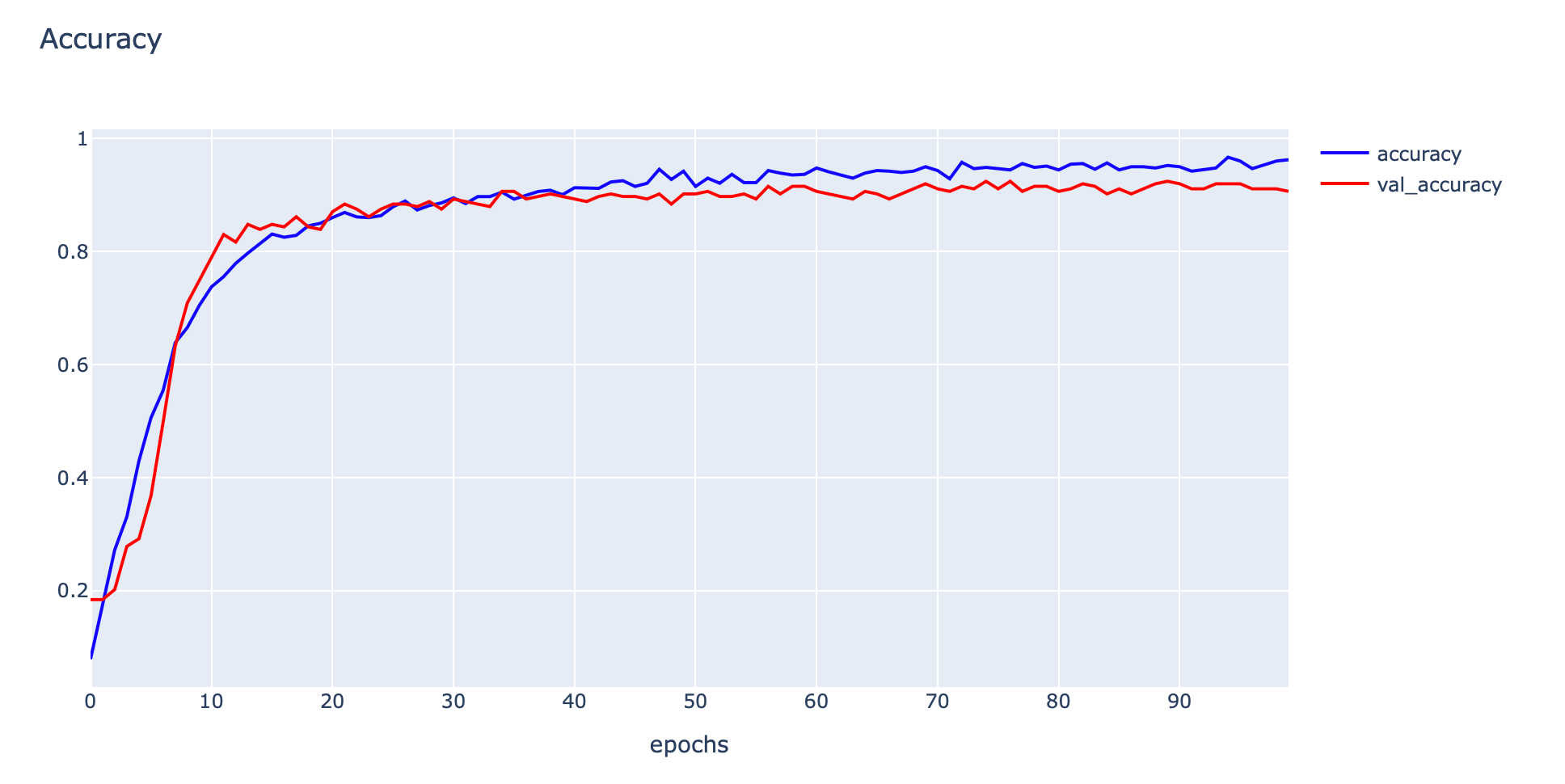
- Load และ Print ชนิดของ Layer, Output Shape และจำนวน Parameter ของ Model
predict_model = load_model(filename)
predict_model.summary()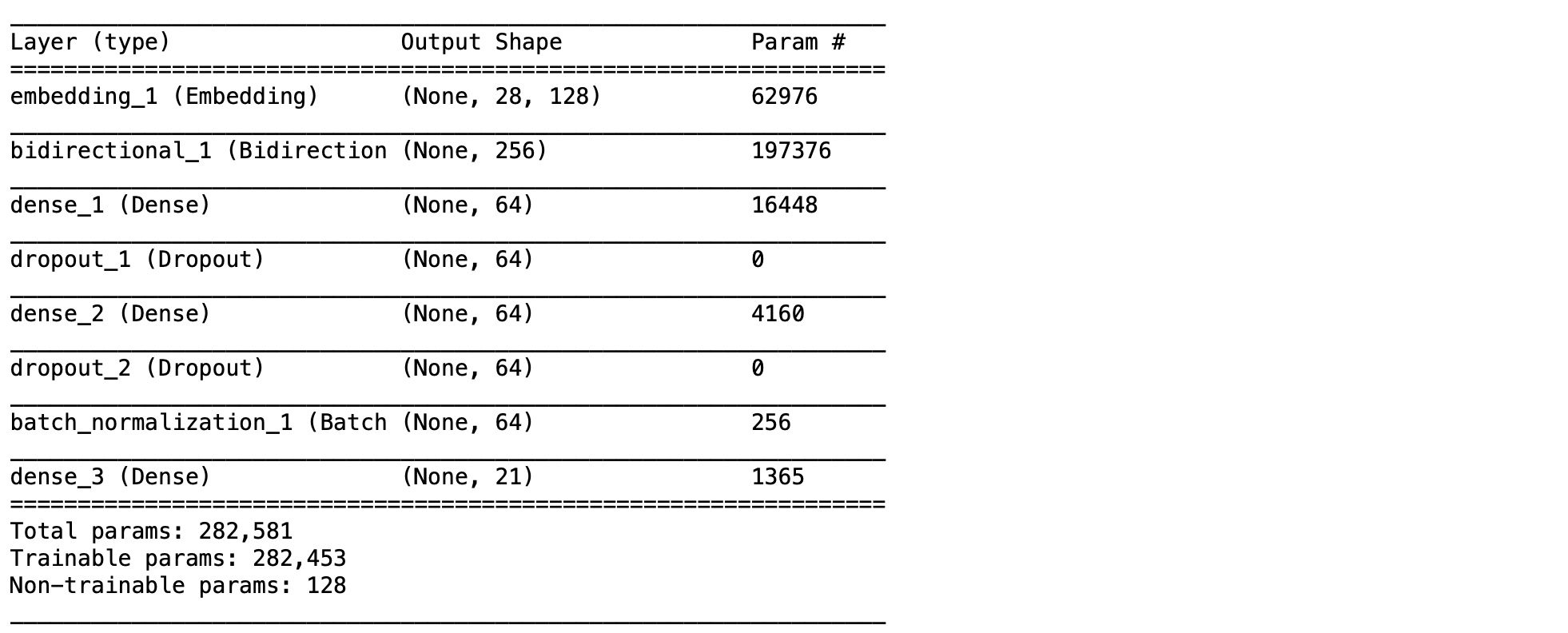
- Evaluate Model
score = predict_model.evaluate(val_X, val_Y, verbose=0)
print('Test loss:', score[0])
print('Test accuracy:', score[1])
- Predict ด้วย Validate Dataset
predicted_classes = predict_model.predict(val_X)
predicted_classes.shape
predicted_classes = np.argmax(predicted_classes,axis = 1)
- เปลี่ยน y_true จาก One Hot กลับเป็นเลขจำนวนเต็มฐานสิบ
y_true = np.argmax(val_Y,axis = 1)
print(val_Y[0])
print(y_true[0])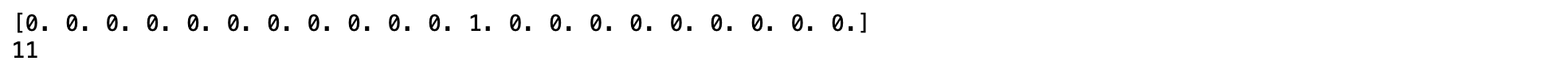
- Save Confusion Matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, predicted_classes)
np.savetxt("confusion_matrix.csv", cm, delimiter=",")- Plot Confusion Matrix
import seaborn as sn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df_cm = pd.DataFrame(cm, range(21), range(21))
plt.figure(figsize=(20,14))
sn.set(font_scale=1.2) # for label size
sn.heatmap(df_cm, annot=True, annot_kws={"size": 14}) # for num predict size
plt.show()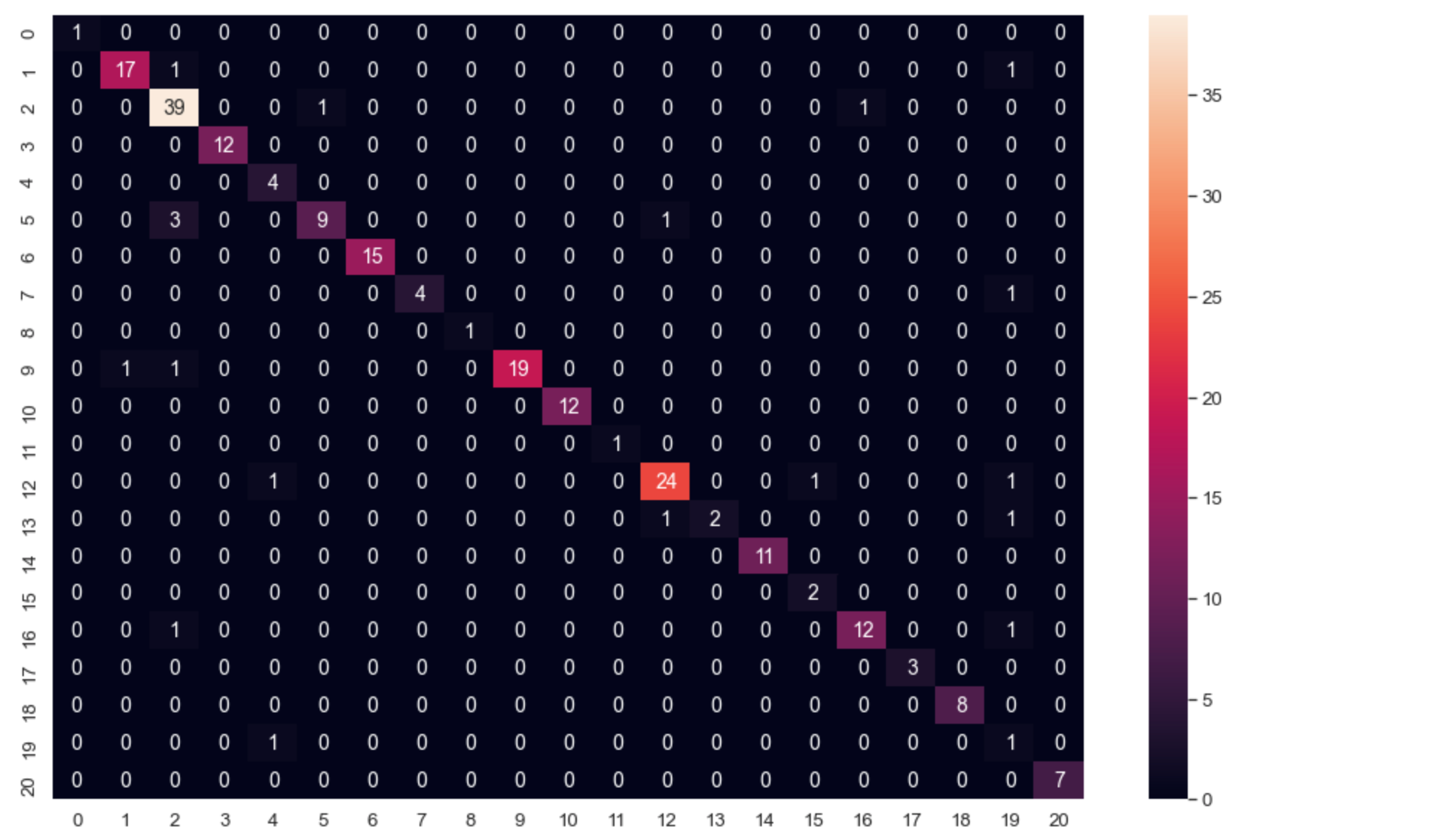
- ดึง Intent ทั้งหมดมาจาก output_tokenizer
label_dict = output_tokenizer.word_index
- ดึงชื่อของ Intent เก็บใน Label
label = [key for key, value in label_dict.items()]
- แสดง Precision, Recall, F1-score
print(classification_report(y_true, predicted_classes, target_names=label, digits=4))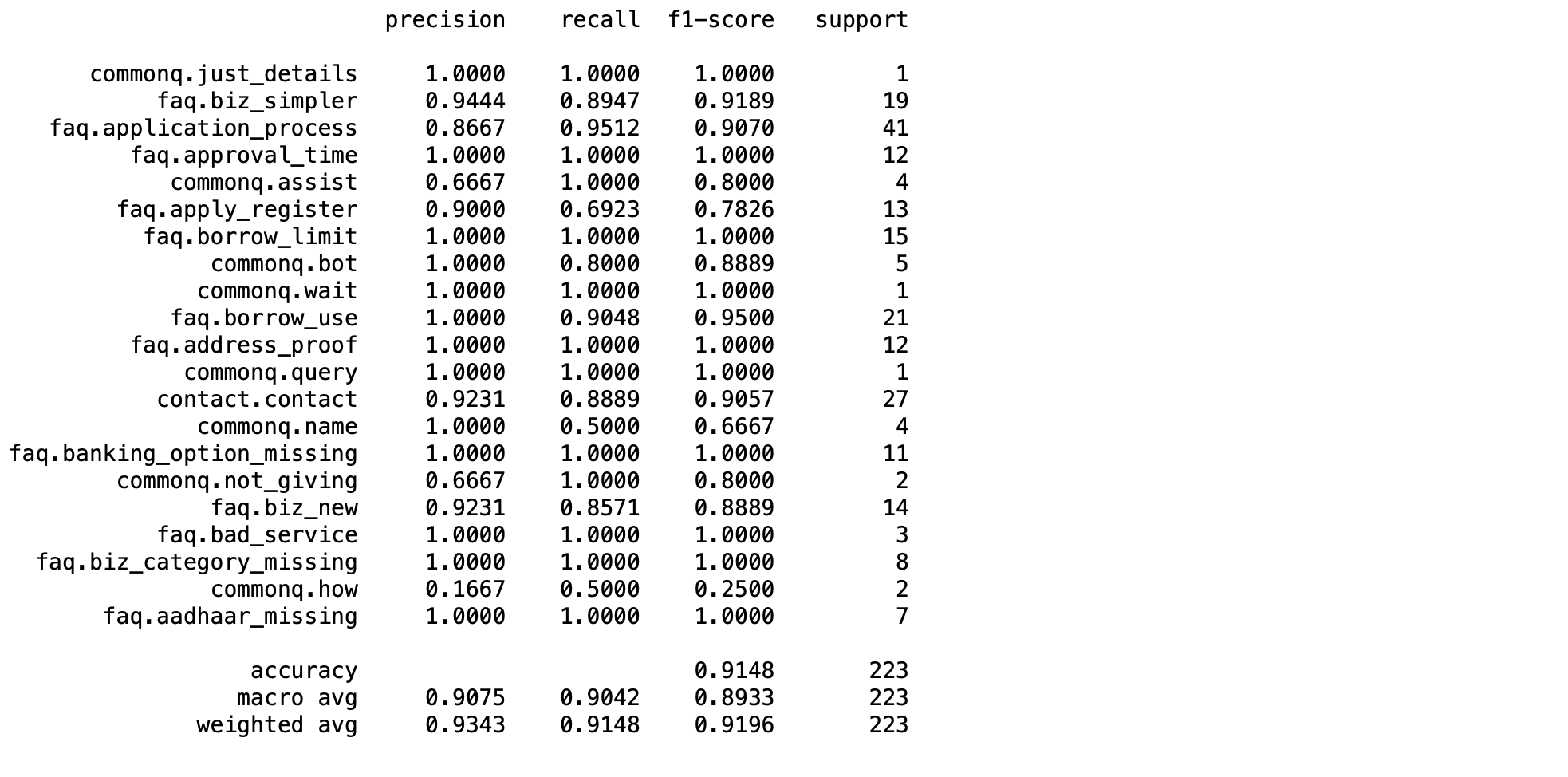
- Save train_word_tokenizer เพื่อใช้ในการ Predict
with open('train_word_tokenizer', 'wb') as file:
p.dump(train_word_tokenizer, file)- Load train_word_tokenizer เพื่อ Predict
with open('train_word_tokenizer', 'rb') as file:
load_train_word_tokenizer = p.load(file)- นิยาม Function Predict
def predictions(text):
clean = re.sub(r'[^\w]', " ", text)
test_word = word_tokenize(clean)
test_word = [w.lower() for w in test_word]
test_ls = train_word_tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(test_word)
print(test_word)
#Check for unknown words
if [] in test_ls:
test_ls = list(filter(None, test_ls))
test_ls = np.array(test_ls).reshape(1, len(test_ls))
x = padding_doc(test_ls, max_length)
pred = predict_model.predict_proba(x)
return pred- Predict และแสดงผลการ Predict แบบ JSON โดยแสดง Sentence, Intent และค่า Confidence
text = "I need help"
pred = predictions(text)
intent_num = np.argmax(pred)
intent = label[intent_num]
confidence = pred[0][intent_num]
res = {'text': text, 'intent': intent, 'confidence': confidence}
print(res)
ลองทำดูครับ
1. เปลี่ยน EPOCH เป็น 500 รอบ Train Model แล้วแสดง
- เวลาในการ Train
- กราฟ Loss/Accuracy
- ตาราง Confusion Matrix
- ตาราง Precision/Recall/F1-score
2. เปลี่ยนชั้น Bidirectional จาก GRU เป็น LSTM (EPOCH = 500) Train Model แล้วแสดง
- เวลาในการ Train
- กราฟ Loss/Accuracy
- ตาราง Confusion Matrix
- ตาราง precision/recall/f1-score
3. เปรียบเทียบประสิทธิภาพระหว่าง GRU และ LSTM ในแง่ เวลา/Loss/Accuracy/Precision/Recall/F1-score
4. อธิปรายประสิทธิภาพ Model ในการ Predict Intent แต่ละ Class